Installing Multiple Agents
Multiple agents can be installed on the same managed machine, each checking in to different KServers.
- A v6 agent can co-exist with v5.1 or older agents.
- A v6 agent can co-exist with other v6 agents.
- Run the v6 agent installer from a different KServer and you will get an additional agent.
- Any managed machine with a domain controller login procedure that runs the agent installer automatically must update the v5.1 or older
KcsSetupfile with the v6 agent. The v5.1 or older installer does not know about the newer v6 agent and will re-install even if the v6 agent is present. - Installing multiple Macintosh agents is not supported.
Driver Usage
If multiple agents are installed on a machine, only one agent at a time controls the drivers required to use File Access, Network Access, Application Blocker. These functions can only be performed by the agent controlling these drivers.
- Originally the first agent installed controls the drivers.
- If the first agent controlling the drivers is uninstalled, then these drivers are uninstalled as well and these three functions cannot be performed by any agent.
- These drivers are re-installed by either of the following events:
- Any of the existing agents on the machine are updated. The updated agent takes control of the drivers and can perform these three functions.
- A new agent is installed. The newly installed agent takes control of these drivers and can perform these three functions.
- To determine which agent has control of the drivers, see Registry below.
Identifying Agents on Managed Machines
When a Kaseya agent is installed, a unique identifier is created for the agent comprising the KServer’s 6 character customer ID and a randomly generated 14 digit number. This unique agent identifier, called the agent GUID, is used to create separate sub-folders to store agent program files, and as a sub-key for agent registry values.
In the examples below, agents display specific information for the following placeholders:
<GUID>- The agent's GUID.<company>- The agent's install directory.<serveraddress>- The KServer address the agent checks into.<machineID.groupID.orgID>- The machine ID, group ID, and organization ID of the agent on the KServer.<shortcutname>- The name of the shortcut. Example:Kaseya Agent #2.
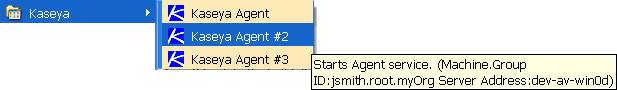
Shortcuts
When you move the mouse cursor over a Kaseya Agent shortcut—for example, a shortcut on the Windows Start Menu—a tool tip displays as:
Start Agent service. (machine.GroupID:<machineID.groupID.orgID> Address:<serveraddress>)- If you right click a shortcut, you'll also see this text in the comment field of the shortcut property page.
About Agent
Right click the K icon ![]() in the system tray of a managed machine and select the About Agent option to display the following information:
in the system tray of a managed machine and select the About Agent option to display the following information:
- Agent Version
- Server Address -
<serveraddress> - Product ID -
<GUID> - Program Title -
<shortcutname>
Add/Remove
Agents display as follows:
Kaseya Agent (<machineID.groupID.orgID> - <serveraddress>)Kaseya Agent #2 (<machineID.groupID.orgID> - <serveraddress>)Kaseya Agent #3 (<machineID.groupID.orgID> - <serveraddress>)
Services
The description field of the service displays the same text shown above in the agent shortcut.
Registry
Agent registry settings displays as follows:
HKLM\Software\Kaseya\Agent
DriverControl - The agent that controls driver usage.
KES_Owned_By - The agent that manages the KES client.
HKLM\Software\Kaseya\Agent\<GUID>
Title - <shortcutname>
Path - C:\Program Files\<company>\<GUID>
ServAddr - <serveraddress>
machineID - <machineID.groupID.orgID>
DriverControl - The agent that controls driver usage.
KES_Owned - The agent that manages the KES client.
Agent Installation Folder
%ProgramFiles%\<company>\<GUID>
Topic 4798: Send Feedback. Download a PDF of this online book from the first topic in the table of contents. Print this topic.