Traverse can monitor Windows hosts using the native Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI), which is installed by default on all Windows 2000, XP and 2003 or later versions, and available as an add-on for other Windows hosts.
Your Traverse Cloud instance includes a WMI Query Server. WMI queries are sent to monitored hosts on TCP/UDP port 135 (which is the DCOM port).
Note: See Configuring Windows WMI for assistance on how to enable WMI on hosts.
Entering Windows Login Credentials Used by WMI
Each Windows host that you want Traverse to monitor through WMI must have a user account that the WMI Query Server can access (with administrative permissions to access various system tables). You can specify these credentials after performing network discovery in Traverse using the Administration > Discovery > New Network Discovery Session link. The following panel displays after network discovery has run and discovered one or more Windows Servers.
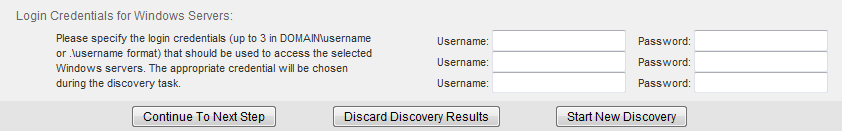
Enter credentials for up to three Windows domains.
Examples
DOMAIN1\username password
DOMAIN2\username password
.\username password
Note: Enter an administrator username in .\username format to access Windows systems that do not belong to a Windows domain. Do not use the localhost\username format.
If the Windows host to be monitored is part of a domain, you will need the username and the corresponding password for a user who is part of the Domain Administrator group. The WMI Query Server will use this user's credentials to connect to the Windows hosts being monitored for retrieving the WMI performance information.