The following is a summary of standard IF-ELSE-STEP commands used in VSA agent procedures.
IF Definitions |
|
Evaluates the given agent variable. See Using Variables. |
|
Adds an Else branch to run steps when an If branch returns a |
|
Compares a variable with a supplied value. |
|
Determines if the current Windows OS is 32 or 64-bit. |
|
Evaluates the total amount of memory reported by the latest audit of the agent. |
|
Evaluates the given registry value. |
|
Tests for the existence of the given registry key. |
|
Checks to see if a specified application is currently running on the managed machine. |
|
Determines if a service is running on the managed machine. |
|
Determines whether the user is either:
|
|
Tests whether a specific user, or any user, is logged in or not. |
|
Presents a Yes/No dialog box to the user. |
|
Tests for the existence of a file. |
|
Tests for the existence of a file in the current directory path returned by getDirectoryPathFromRegistry(). |
|
Always returns |
|
STEP Definitions |
|
Suppresses alarms on a machine for a specified number of minutes. |
|
Stops the suppression of alarms on a machine. |
|
Captures a desktop screenshot of the agent machine and uploads it to the Kaseya Server. |
|
Changes a domain user's membership in a domain user group. |
|
Changes a local user's membership in a local user group. |
|
Closes a running application. |
|
Adds a one-line comment to the procedure. |
|
Copies a file from one directory to another. |
|
Copies a file from one directory to another using a user credential. |
|
Adds a new user to an Active Directory domain when run on a domain controller. |
|
Creates an event log entry in either the Application, Security or System event log types. You can create a Warning, Error or Informational event with your own description. |
|
Adds a new local user account to a machine. |
|
Creates a new file share on a Windows machine. |
|
Deletes a directory from the agent machine. |
|
Deletes a file from the managed machine. |
|
Deletes file in directory returned by getDirectoryPathFromRegistry(). |
|
Deletes a key from the registry. |
|
Deletes a 64-bit key from the registry. |
|
Deletes a value from the registry. |
|
Deletes a 64-bit value from the registry. |
|
Deletes a user from the agent machine. |
|
Disables a user, preventing logon to the agent machine. |
|
Disables a Windows service. |
|
Enables a previously disabled user, allowing the user to logon to the OS. |
|
Executes any file as if it was run from the Run item in the Windows Start menu. |
|
Same as execute file. File location is relative to the directory returned by getDirectoryPathFromRegistry(). |
|
Executes a powershell file, or command with arguments or both. |
|
Executes a powershell file, or command with arguments or both, as a 32 bit system command. |
|
Executes a powershell file, or command with arguments or both, as a 32 bit user command. |
|
Executes a powershell file, or command with arguments or both, as a 64 bit system command. |
|
Executes a powershell file, or command with arguments or both, as a 64 bit user command. |
|
Starts another VSA agent procedure on the current machine. |
|
Runs any command from a command shell. |
|
Executes a shell command and returns output created during and after its execution to a variable. |
|
Runs a Vbscript, with or without command line arguments. |
|
Returns the directory path stored in the registry at the specified location. Result used in subsequent steps. |
|
Gets a file from the managed machine and saves it to the Kaseya Server. |
|
Gets a file from the managed machine located relative to the directory returned by getDirectoryPathFromRegistry() and saves it to the Kaseya Server. |
|
Returns the text and HTML contents of a URL and stores it to a file on the managed machine. |
|
Downloads a file from a given URL to a target folder and file for that agent. Uses the Patch Management > File Source settings. |
|
Gets a value from the agent on the managed machine and assigns it to a variable. See Using Variables. |
|
Generates a random number. |
|
Gets a variable that persists outside of the immediate procedure's execution. |
|
Reads up to three variables you have previously created using the getVariableUniversalCreate() step. |
|
Adds the current user to the local administrator’s group on the agent machine, either permanently or for a temporary period of time. |
|
Specifies the user account to use when executing a file or shell when Execute as the logged on user is specified in a subsequent command. |
|
Silently installs a package using the |
|
Silently installs a Debian package on any Linux OS that supports |
|
Silently installs a |
|
Installs an MSI file for Windows. |
|
Silently installs a |
|
Silently installs an RPM package on any Linux OS that supports installing RPMs. |
|
Automatically logs off the current user. |
|
Pauses the procedure for N seconds. |
|
Reboots the managed machine. |
|
Reboots a machine, displaying a warning message to the end-user before the reboot process occurs. |
|
Removes a file share from a Windows agent. |
|
Renames a file that is currently in use. |
|
Renames a file currently in use in directory returned by getDirectoryPathFromRegistry(). |
|
Schedules an agent procedure to run on a specified machine. |
|
Creates an alert based on a previous getVariable() command. |
|
Sends an email to one or more recipients. |
|
Displays a message in a dialog box on the managed machine. |
|
Opens a browser to the specified URL on the managed machine. |
|
Sets the registry value to a specific value. |
|
Sets the 64-bit registry value to a specific value. |
|
Returns a value from the database and stores it to a named variable by running a selected SQL "read" statement. |
|
Updates the database by running a selected SQL "write" statement. |
|
Runs a Start command for a Windows service, if it exists. |
|
Runs a Start command for a Windows service if it exists. |
|
Transfers a file from the agent machine running this step to another agent machine. |
|
Silently uninstalls a product based on its MSI GUID. |
|
Extracts the contents of a specified zip file to a target folder. |
|
Updates the selected System Info field with the specified value. |
|
Specifies that Set Credential should be used when Execute as the logged on user is specified in a subsequent command. |
|
Sets the Service Recovery Settings for any given service in Windows. |
|
Writes a directory from the server to the managed machine. |
|
Writes a file stored on the Kaseya Server to the managed machine. |
|
Transfers a file from another agent machine to the agent machine running this step. |
|
Writes a file stored on the Kaseya Server to the managed machine using the directory returned by getDirectoryPathFromRegistry(). |
|
Writes a string to the Agent Procedure Log. |
|
Writes text to a file on the agent machine. |
|
Compresses a directory and any subdirectories or files it contains into a zip file on the agent machine. |
|
Compresses a single file or files into a zip file on the agent machine. |
|
IF Commands
checkVar()
Enter a variable name, in the form #var_name#, in the space provided. checkVar() evaluates the current values assigned #var_name# and compares it with the supplied value. The supplied value may also be another variable name in the form of #var_name2#. If the check is true, IF commands are executed. If the check is false, ELSE steps are executed. See Using Variables. The available tests are:
Exists : true if the variable exists.Does Not Exist : true if the variable does not exist.= : true if value of the variable equals the test value.Not = : true if value of the variable does not equal the test value.> : true if value of the variable is greater than the test value.>= : true if value of the variable is greater than or equal to the test value.< : true if value of the variable is less than the test value.<= : true if value of the variable is less than or equal to the test value.Contains : true if the test value is a sub string of the variable value.Not Contains : true if the test value is not a sub string of the variable value.Begins With : true if the variable value begins with the test value.Ends With : true if the variable value ends with the test value.For the tests =, Not =, >, >=, <, and <= the variables compared may be a string, a number, a date in the format of yyyy/mm/dd or yyyy/mm/dd hh:mm or yyyy/mm/dd hh:mm:ss, or a version number containing dots or commas such as 1.2.3 or 4,5,6,7. Values in variables are stored as strings, so compared numbers must be of equal string length. If a date format is specified, it may be offset using + dd:hh:mm:ss or - dd:hh:mm:ss. Only dd days are required; hh hours, mm minutes, and ss seconds may be omitted and are assumed to be zero when absent. CURRENT_TIMESTAMP may be specified to indicate that the current time be substituted in the comparison at the time the procedure is executed. e.g. CURRENT_TIMESTAMP - 7:12:00:00 will be evaluated as 7 days and 12 hours subtracted from the time that the procedure is executed.
else
Adds an Else command underneath a corresponding If command. Any steps listed under the Else command are executed when the corresponding If command returns a False result.
eval()
Enter an expression containing one or more variable names, in the form #var_name#, in the space provided. eval() uses the current value assigned to each #var_name#, evaluates the mathematical expression, and compares it with the supplied value. The supplied value may also be another expression. The mathematical expression may contain +, -, *, /, (, and ). e.g. (3.7 + (200 * #countA#)) / (#countB# - #countC#). If the check is true, IF steps are executed. If the check is false, ELSE steps are executed. The available tests are:
= : true if value of the variable equals the test value.Not = : true if value of the variable does not equal the test value.> : true if value of the variable is greater than the test value.>= : true if value of the variable is greater than or equal to the test value.< : true if value of the variable is less than the test value.<= : true if value of the variable is less than or equal to the test value.Note: Cannot be used with Exists, Does Not Exist, Contains, or Not Contains operators.
getOS()
Determines if the current Windows OS is 32 or 64-bit.
Operating systems supported: Windows
getRAM()
Evaluates the total amount of memory reported by the latest audit of the agent. This could come in helpful in ensuring a system meets the resource requirements of an application before an installation is attempted.
Operating systems supported: Windows, OS X, Linux
getRegistryValue() / get64BitRegistryValue()
After entering the registry path, the value contained in the key is returned. A check can be made for existence, absence, equality, or size differences. For example, HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\AppPaths\AgentMon.exe\path contains the directory path identifying where the agent is installed on the target machine. The test determines if the value stored for this key exists, thereby verifying the agent is installed.
The available tests are:
Exists : true if the registry key exists in the hive.Does Not Exist : true if the registry key does not exist in the hive.= : true if value of the registry key equals the test value.Not = : true if value of the registry key does not equal the test value.> : true if value of the registry key is greater than the test value (value must be a number).>= : true if value of the registry key is greater than or equal to the test value (value must be a number).< : true if value of the registry key is less than the test value (value must be a number).<= : true if value of the registry key is less than or equal to the test value (value must be a number).Contains : true if the test value is a sub string of the registry key value (value must be a string).Not Contains : true if the test value is not a sub string of the registry key value (value must be a string).Using the Backslash Character (\)
A backslash character \ at the end of the key returns the default value of that key. HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\App Paths\WORDPAD.EXE\ returns a default value, such as %ProgramFiles%\Windows NT\Accessories\WORDPAD.EXE
The last single backslash in a string is used to delimit the registry key from the registry value. To include backslashes as part of the value string, specify double slashes for each slash character. For example, the string HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\SomeKey\Value\\Name is interpreted as the key HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\SomeKey with a value of Value\Name.
hasRegistryKey() / has64bitRegisterKey()
Tests for the existence of a registry key. hasRegistryKey() differs from getRegistryValue() since it can check for a directory level registry entry that only contains more registry keys (no values).
isAppRunning()
Checks to see if a specified application is currently running on the managed machine. If the application is running, the IF command is executed; otherwise, the ELSE command is executed. When this option is selected from the drop-down list, the Enter the application name field appears. Specify the process name for the application you want to test. For example, to test the Calculator application, specify calc.exe, which is the process name that displays in the Processes tab of the Windows Task Manager.
isServiceRunning()
Determines if a service is running on the managed machine. Specify the service name.
Note: Be sure to use the service name of the service, not the display name of the service. For example, the display name of the service for Microsoft SQL Server is SQL Server (MSSQLSERVER), but the service name of the service is MSSQLSERVER. For Windows machines, right click any service in the Services window and click the Properties option to see the service name of that service.
isUserActive()
Determines whether the user is either:
Operating systems supported: Windows, OS X, Linux
isUserLoggedin()
Tests to see if a specific user or any user is logged on the managed machine. Enter the machine user's logon name or leave the field blank to check for any user logged on. The IF commands are executed if a user is logged on. The ELSE steps are executed if the user is not logged on.
isYesFromUser()
Displays a dialog box on the managed machine with Yes and No buttons. Also carries out the ELSE command if a specified amount of time has timed out. If Yes is selected by the machine user, the IF command is executed. If the selection times out or the machine user selects No, the ELSE command is executed. This function requests the machine user's permission to proceed with the agent procedure. This query is useful for agent procedures that require a reboot of the managed machine before completion.
Procedure variables, for example #varName#, may be used inside isYesFromUser() fields to dynamically generate messages based on procedure data.
testFile()
Determines if a file exists on a managed machine. Enter the full path and file name. testFile() compares the full path and file name with the supplied value. If the check is true, IF commands are executed. If the check is false, ELSE steps are executed.
Note: Environment variables such as %windir%\notepad.exe are acceptable.
The available tests are:
Exists : true if the full path and file name exists.Does not Exist : true if the full path and file name does not exist.Contains : true if the test value is a sub string of the file content.Not Contains : true if the test value is not a sub string of the file content.Begins With : true if the test value begins with the variable value.Ends With : true if the test value ends with the variable value.testFileInDirectoryPath()
Tests the specified file located at the path returned using the getDirectoryPathFromRegistry() step. The available tests are:
Exists : true if the file name exists.Does not Exist : true if the file name does not exist.Contains : true if the test value is a sub string of the file content.Not Contains : true if the test value is not a sub string of the file content.Begins With : true if the test value begins with the variable value.Ends With : true if the test value ends with the variable value.true
Selecting True directs the IF commands to execute. Use True to directly execute a series of steps that do not require any decision points, such as determining whether a file exists using testFile().
STEP Commands
alarmsSuspend()
Suppresses alarms on a machine for a specified number of minutes. Updates the status of machines on the Monitor > Status > Suspend Alarm page.
alarmsUnsuspendAll()
Stops the suppression of alarms on a machine. Updates the status of machines on the Monitor > Status > Suspend Alarm page.
captureDesktopScreenshot()
Captures a desktop screenshot of the agent machine and uploads it to the Kaseya Server. The screenshot is saved as a PNG file with a unique name in a folder dedicated to that agent. You can access these files from the Audit > Documents page or from Live Connect. End-user notification options must be selected based on the level of user notification desired, silently capturing a screenshot, notifying the user that the capture will take place, or asking to approve the capture. A custom message can be entered if end-user notification or permission requesting is selected. Otherwise a standard message displays.
Operating systems supported: Windows, OS X
changeDomainUserGroup()
Changes a domain user's membership in a domain user group. This STEP must be run on a domain controller. Enter the domain username of the member being added or removed from the domain user group. Then select whether to add or remove membership. Then select the domain user group.
Operating systems supported: Windows
changeLocalUserGroup()
Changes a local user's membership in a local user group. Enter the local username of the member being added or removed from the local user group. Then select whether to add or remove membership. Then select the group.
Operating systems supported: Windows
closeApplication()
If the specified application is running on the managed machine, then that application is closed down. Specify the process name for the application you want to close. For example, to close the Calculator application, specify calc.exe, which is the process name that displays in the Processes tab of the Windows Task Manager.
comment()
Adds a one line comment to the procedure.
copyFile()
Copies a file from one directory to another on the agent machine. If the target file exists, you must check a box to overwrite an existing file. Be sure to keep in mind folder syntax when running this STEP across different operating systems, for example, c:\temp\tempfile.txt for Windows and /tmp/tempfile.txt for OS X and Linux.
Operating systems supported: Windows, OS X, Linux
copyUseCredentials()
Copies a file from a directory on a machine and attempts to copy the file to a target directory and filename. The copy process uses either:
This STEP is mostly used for accessing files across network UNC shares. If the target file exists, you must check a box to overwrite an existing file. Be sure to keep in mind folder syntax when running this STEP across different operating systems, for example, c:\temp\tempfile.txt for Windows and /tmp/tempfile.txt for OS X and Linux.
Operating systems supported: Windows, OS X, Linux
createDomainUser()
Adds a new user to an Active Directory domain when run on a domain controller. Enter a domain user name to create, then a password that meets the domain's complexity requirements for user accounts, then select the domain group the user will be added to, either Domain Users or Domain Admins.
Operating systems supported: Windows
createEventLogEntry()
Creates an event log entry in either the Application, Security or System event log types. You can create a Warning, Error or Informational event with your own description. The created event is hard-coded to use an Event ID of 607.
Operating systems supported: Windows
createLocalUser()
Adds a new local user account to a machine. Enter a local user name to create, then a password that meets local user account complexity requirements, then select the group the user will be added to.
Operating systems supported: Windows, OS X, Linux
createWindowsFileShare()
Creates a new file share on a Windows machine. You must type in the name of the file share as it will be accessed over the network, and enter the source folder on the agent for the file share. This folder will be created if it does not yet exist.
Operating systems supported: Windows
deleteDirectory()
Deletes a directory from an agent machine. Ensure you have your directory syntax correct for Windows vs. OS X/ Linux. To ensure all sub-directories and files are also removed, check the Recursively delete subdirectories and files checkbox.
Operating systems supported: Windows, OS X, Linux
deleteFile()
Deletes a file on a managed machine. Enter the full path and filename.
Note: Environment variables are acceptable if they are set on a user's machine. For example, using a path %windir%\notepad.exe would be similar to C:\windows\notepad.exe.
Note: You can delete a file that is currently in use using the renameLockedFile() command.
deleteFileInDirectoryPath()
Deletes the specified file located at the path returned using the getDirectoryPathFromRegistry() command.
deleteRegistryKey() / delete64BitRegistryKey()
Deletes the specified registry key and all its sub-keys.
deleteRegistryValue() / delete64BitRegistryValue()
Deletes the value stored at the specified registry key. The last single backslash in a string is used to delimit the registry key from the registry value. To include backslashes as part of the value string, specify double slashes for each slash character. For example, the string HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\SomeKey\Value\\Name is interpreted as the key HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\SomeKey with a value of Value\Name.
deleteUser()
Deletes a user from the agent machine.
Operating systems supported: Windows, OS X, Linux
disableUser()
Disables a user, preventing logon to the agent machine.
Operating systems supported: Windows, OS X, Linux
disableWindowsService()
Disables a Windows service.
Operating systems supported: Windows
enableUser()
Enables a previously disabled user, allowing the user to logon to the OS.
Operating systems supported: Windows, OS X
executeFile()
Executes the specified file on the managed machine. This function replicates launching an application using the Run… command located in the Microsoft Windows Start menu. This function takes three parameters:
.exe file..exe file.exe completes or not. Note: Environment variables are acceptable, if they are set on a user's machine. For example, using a path %windir%\notepad.exe, would be similar to C:\windows\notepad.exe.
If Execute as the logged on user is selected, then a credential must be specified by running either the impersonateUser() or useCredential() command before this command. If run Execute as the system account is selected, execution is restricted to the agent's system level access.
executeFileInDirectoryPath()
Same as Execute File except the location of the .exe file is located at the path returned from a getDirectoryPathFromRegistry() command.
If Execute as the logged on user is selected, then a credential must be specified by running either the impersonateUser() or useCredential() command before this command. If run Execute as the system account is selected, execution is restricted to the agent's system level access.
executePowershell()
Executes a powershell script, including:
.PS1 fileOperating systems supported: Windows XP SP3+/Server 2008 with Powershell add-on, Windows 7, Windows Server 2008
There are five variants of this command available.
System and user commands:
executeProcedure()
Causes another named procedure to execute. Use this capability to string multiple IF-ELSE-STEP procedures together. If the procedure no longer exists on the Kaseya Server, an error message displays next to the procedure drop-down list. You can use this command to run a system procedure. You can nest procedures to 10 levels.
executeShellCommand()
Allows the procedure to pass commands to the command interpreter on the managed machine. When this command is selected, the field Enter the command to execute in a command shell is displayed. Enter a command in the field. The command must be syntactically correct and executable with the OS version on the managed machine. Commands and parameters containing spaces should be surrounded by quotes. Since the command is executed relative to the agent directory, absolute paths should be used when entering commands.
Note: executeShellCommand() opens a command prompt window on a managed Windows machine to execute in. If you do not want a window opening on a managed Windows machine, because it might confuse users, put all the commands in a batch file. Send that file to the managed Windows machine using the writeFile() command. Then run the batch file with the executeFile() command. executeFile() does not open a window on a managed Windows machine.
If Execute as the logged on user is selected, then a credential must be specified by running either the impersonateUser() or useCredential() command before this command. If run Execute as the system account is selected, execution is restricted to the agent's system level access.
executeShellCommandToVariable()
Executes a shell command and returns output created during and after its execution to a variable. The variable must be referred to in subsequent steps as #global:cmdresults#.
Operating systems supported: Windows, Linux, OS X
executeVBScript()
Runs a Vbscript, with or without command line arguments. If the Vbscript displays a popup window or notifies the end user, check the box for Use Wscript instead of Cscript.
Operating systems supported: Windows
getDirectoryPathFromRegistry()
Returns a file path stored in the specified registry key. Use this command to fetch the file location. For instance, use this command to find the directory where an application has been installed. The result can be used in subsequent steps by:
getFile()
Upload the file at the specified path from the managed machine. Be sure to enter a full path filename that you want to upload. Example: news\info.txt. Folders are created when the getFile() command is run, if they don't already exist. The file is stored on the Kaseya Server in a private directory for each managed machine. View or run the uploaded file using Agent Procedures > Get File.
.bak extension prior to the next upload of the file. This allows you to examine both the latest version of the file and the previous version.getFileInDirectoryPath()
Just like the getFile() command but it adds the path returned from the getDirectoryPathFromRegistry() command to the beginning of the remote file path. Access the uploaded file using the Agent Procedures > getFile() function.
getURL()
Returns the text and HTML contents of a URL and stores it to a file on the managed machine. To demonstrate this to yourself, try specifying www.kaseya.com as the URL and c:\temp\test.htm as the file to store the contents of this URL. A copy of the web page is created on the managed machine that contains all of the text and HTML content of this webpage. You can search the contents of the file on the managed machine in a subsequent command.
Another use is to download an executable file that is available from a web server, so that you don't need to upload the file to the VSA server nor use the VSA's bandwidth to write the file down to each agent. You can use a subsequent command to run the downloaded executable on the managed machine.
Note: This command can download files from a LAN file source instead of the URL using Agent > Configure Agents > LAN Cache. Files have to be larger than 4k bytes.
getURLUsePatchFileSource()
Downloads a file from a given URL to a target folder and file for that agent. Uses the Patch Management > File Source settings.
Operating systems supported: Windows
getVariable()
Defines a new agent variable. When the procedure step executes, the system defines a new variable and assigns it a value based on data fetched from the managed machine's agent.
Note: See Using Variables for the types of variable values supported by the getVariable() command.
getVariableRandomNumber()
Generates a random number which can then be accessed as the variable #global:rand# in a subsequent step.
Operating systems supported: Windows, OS X, Linux
getVariableUniversalCreate()
Gets a variable that persists outside of the immediate procedure's execution. This can be useful for passing a variable to another agent procedure using the scheduleProcedure() step. You can create up to three variables. You can enter either string data or variables created in an earlier step. Variables created using this step can only be read using the Get Variable – Universal – Read step in any subsequent step.
Operating systems supported: Windows, OS X, Linux
getVariableUniversalRead()
Reads up to three variables you have previously created using the Get Variable – Universal – Create step. These variables must be referred to as #global:universal1#, #global:universal2#, and #global:universal3#. Please see the initial Get Variable – Universal – Create step for more detail.
Operating systems supported: Windows, OS X, Linux
giveCurrentUserAdminRights()
Adds the current user to the local administrator’s group on the agent machine, either permanently or for a temporary period of time. This change does not take effect until the user logs off. It is recommended you leverage the logoffCurrentUser() step.
Operating systems supported: Windows
impersonateUser()
Enter a username, password, and domain for the agent to logon with. This command is used in a procedure before an executeFile(), executeFileInDirectoryPath() or executeShellCommand() that specifies the Execute as the logged on user option. Leave the domain blank to log into an account on the local machine. Use impersonateUser() to run an agent procedure using a credential specified by agent procedure. Use useCredential() to run an agent procedure using a credential specified by managed machine.
installAptGetPackage()
Silently installs a package using the apt-get command in Linux.
Operating systems supported: Linux
installDebPackage()
Silently installs a Debian package on any Linux OS that supports .deb packages.
Operating systems supported: Linux
installDMG()
Silently installs a .DMG package in OS X. If the package is formatted as an Application, it is copied to the /Applications folder. If the .DMG contains a .PKG installer within it, Kaseya attempts to install it.
Operating systems supported: OS X
installMSI()
Installs an MSI file for Windows. Options can be selected to either run a quiet installation or to avoid automatically restarting the computer after installation if it is requested.
Operating systems supported: Windows
installPKG()
Silently installs a .PKG package in OS X.
Operating systems supported: OS X
installRPM()
Silently installs an RPM package on any Linux OS that supports installing RPMs.
Operating systems supported: Linux
logoffCurrentUser()
Automatically logs off the current user. An optional warning that the log-off process is about to begin can be entered and displayed to the end-user.
Operating systems supported: Windows, OS X
pauseProcedure()
Pause the procedure for N seconds. Use this command to give Windows time to complete an asynchronous task, like starting or stopping a service.
reboot()
Unconditionally reboots the managed machine. To warn the user first, use the isYesFromUser() command before this command. A isYesFromUser() command prompts the user before rebooting their machine.
rebootWithWarning()
Reboots a machine, displaying a warning message to the end-user before the reboot process occurs.
Operating systems supported: Windows, OS X
removeWindowsFileShare()
Removes a file share from a Windows agent.
Operating systems supported: Windows
renameLockedFile()
Renames a file that is currently in use. The file is renamed the next time the system is rebooted. The specified filename is a complete file path name. Can be used to delete a file that is currently in use if the "new file name" is left blank. The file is deleted when the system is rebooted.
renameLockedFileInDirectoryPath()
Renames a file that is currently in use that is located in the path returned from a getDirectoryPathFromRegistry() command. The file is renamed the next time the system is rebooted. Can be used to delete a file that is currently in use if the "new file name" is left blank. The file is deleted when the system is rebooted.
scheduleProcedure()
Schedules a procedure to run on a specified machine. Optionally specifies the time to wait after executing this step before running the procedure and the specified machine ID to run the procedure on. If no machine is specified, then the procedure is run on the same machine running the agent procedure. Enter the complete name of the machine, for example, machine.unnamed.org. This command allows an agent procedure running on one machine to schedule the running of an agent procedure on a second machine. You can use this command to run a system procedure. You can nest procedures to 10 levels.
sendAlert()
This step command takes no parameters. Instead one or more getVariable() steps—run prior to the sendAlert() step—specify alert action variables that determine the actions triggered by the sendAlert() step. All alert action variables are optional. If no alert action variables are defined, an alarm will be created with a system default message. An alert action variable can be used to disable the default alarm action. Alert action variables, if used, must use the specific names corresponding to their actions:
alertSubject - Subject for alert message. A system default message is used if you do not define one in the agent procedure. See System Parameters below.alertBody - Body for alert message. A system default message is used if you do not define one in the agent procedure. See System Parameters below.alertDisableAlarm - When a default alarm enabled, enter any value to disable.alertGenerateTicket - Enter any value to generate.alertScriptName - Valid agent procedure name to execute on current machine.alertEmailAddressList - Comma-separated email addresses. Required to send email.alertAdminNameList - Comma-separated list of VSA user names. Required to send messages to the Info Center > Inbox.alertNotificationBarList - Comma-separated list of VSA user names. Required to send messages to the Notification Bar.alertNotificationBarMasterAdmins - Enter any value to send notifications to the Notification Bar for all master users.System Parameters
You can override the default alertSubject and alertBody text sent by the sendAlert() command. If you do you can embed the following system parameters in the alertSubject and alertBody variables you create using getVariable() commands. Double angle brackets are required when embedding them in text. You do not create these embedded system parameters using a getVariable() command. They are always available.
<<id>> - Machine display name on which the agent procedure is being executed.<<gr>> - Machine group name on which the agent procedure is being executed.<<at>> - Alert date/time (server time).<<ata>> - Alert date/time (agent time).<<apn>> - Agent procedure name being executed.Custom Parameters
You can embed custom parameters in alertSubject and alertBody getVariable() commands. First, create another variable using the getVariable() command. The value stored with this first variable can be dynamic, determined when the agent procedure is run. Second, insert the name of this first variable—surrounded by # and # brackets—into the text value specified by the alertSubject and alertBody getVariable() commands. Examples include:
#filename##logentry##registrykey##registryvalue#Specifying getVariable() Commands before sendAlert() in an Agent Procedure
For example, assume an agent procedure:
runTimeVar using the getVariable() command. The values entered are:Constant ValueProcedure terminated. Could not access 'File Server 123'.runTimeVarAll Operating SystemsContinue on FailConstant ValueThis alert was generated by <<apn>> on machine <<id>> at <<ata>>: #runTimeVar#.alertBodyAll Operating SystemsContinue on FailNote: The sequence of parameter variables and alert action variables does not matter. But all of them have to run before the sendAlert() command that makes use of them.
sendEmail()
Sends an email to one or more recipients. Specifies the subject and body text of the email.
sendMessage()
Sends the entered message to a managed machine. An additional checkbox, if checked, sends the message immediately. If unchecked, sends the message after the user clicks the flashing agent system tray icon.
sendURL()
Displays the entered URL in a web browser window on the managed machine. An additional checkbox, if checked, displays the URL immediately. If unchecked, the URL is displayed after the user clicks the flashing agent system tray icon.
setRegistryValue() / set64BitRegistryValue()
Writes data to the specified registry value. This function takes three parameters:
(Default) value for a registry key by adding a trailing backslash \. Otherwise specify a name for an existing value or to create a new value. See the Name column in image below. (Default) value: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\000Sample\ HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\SomeKey\Value\\Name is interpreted as the key HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\SomeKey with a value of Value\Name.REG_SZ - String value.REG_BINARY - Binary data displayed in hexadecimal format.DWORD - Binary data limited to 32 bits. Can be entered in hexadecimal or decimal format.REG_EXPAND_SZ - An "expandable" string value holding a variable. Example: %SystemRoot%. REG_MULTI_SZ - A multiple string array. Used for entering more than one value, each one separated by a \0 string. Use \\0 to include \0 within a string array value.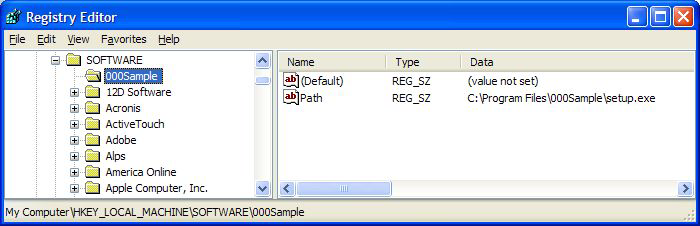
sqlRead()
Returns a value from the database and stores it to a named variable by running a selected SQL "read" statement. Global "read" statements are specified in the following location: <KaseyaInstallationDirectory>\xml\Procedures\AgentProcSQL\0\SQLRead\<filename.xml> Filenames can be any name with an .xml extension so long as they are formatted correctly internally. Multiple statements specified using one or more XML files display as a single combined combo box list in the user interface. Each SQL statement in the XML file has a unique label, and only the labels are shown in the combo box. If no SQL statements are defined, then *No Approved SQL* displays in the combo box.
Partition-Specific Statements
Partition-specific folders can contain partition-specific SQL statements. For example: <KaseyaInstallationDirectory>\xml\Procedures\AgentProcSQL\123456789\SQLRead\<filename.xml>. Users can select and run all 0 folder SQL "read" statements and all SQL "read" statements located in the partition path that matches the partition they are using.
Example Format
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<queryList>
<queryDef label="Agent Machine Name" sql="SELECT machName FROM dbo.machNameTab WHERE agentGuid = #vMachine.agentGuid#" />
</queryList>
sqlWrite()
Updates the database—such as updating the value in a column or inserting a row—by running a selected SQL "write" statement. Global "write" statements are specified in the following location: <KaseyaInstallationDirectory>\xml\Procedures\AgentProcSQL\0\SQLWrite\<filename.xml> Filenames can be any name with an .xml extension so long as they are formatted correctly internally. Multiple statements specified using one or more XML files display as a single combined combo box list in the user interface. Each SQL statement in the XML file has a unique label, and only the labels are shown in the combo box. If no SQL statements are defined, then *No Approved SQL* displays in the combo box.
Partition-Specific Statements
Partition-specific folders can contain partition-specific SQL statements. For example: <KaseyaInstallationDirectory>\xml\Procedures\AgentProcSQL\123456789\SQLWrite\<filename.xml>. Users can select and run all 0 folder SQL "write" statements and all SQL "write" statements located in the partition path that matches the partition they are using.
Example Format
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<queryList>
<queryDef label="Update Table" sql="UPDATE table1 SET column2 = value2 WHERE column1 = value1" />
</queryList>
startWindowsService()
Runs a Start command for a Windows service, if it exists.
Operating systems supported: Windows
stopWindowsService()
Runs a Stop command for a Windows service if it exists.
Operating systems supported: Windows
transferFile()
Transfers a file from the agent machine running this step to another agent machine. Enter the fully qualified machine ID of the target machine, for example, mymachine.root.kaseya. Then enter the full path and file name of the source file you wish to send from the currently selected agent. Then enter the full path and file name of the target file on the target machine.
Operating systems supported: Windows
uninstallbyProductGUID()
Silently uninstalls a product based on its MSI GUID.
Operating systems supported: Windows
unzipFile()
Extracts the contents of a specified zip file to a target folder, with an option to automatically overwrite any previously existing target files or folders.
Operating systems supported: Windows, OS X, Linux
updateSystemInfo()
Updates the selected System Info field with the specified value for the machine ID this procedure runs on. The System Info fields you can update include all columns in vSystemInfo except agentGuid, emailAddr, Machine_GroupID, machName, and groupName. vSystemInfo column information is used by Audit > System Info, Agent > System Status, the Filter Aggregate Table in View Definitions, and the Aggregate Table report.You can update a System Info field using any string value, including the value of any previously defined agent procedure variable.
useCredential()
Uses the credentials set for the machine ID in Set Credential. This command is used in a procedure before an executeFile(), executeFileInDirectoryPath() or executeShellCommand() that specifies the Execute as the logged on user option. Also used to access a network resource requiring a credential from a machine when a user is not logged on. Use impersonateUser() to run an agent procedure using a credential specified by agent procedure. Use useCredential() to run an agent procedure using a credential specified by managed machine.
Note: A procedure execution error is logged if a Set Credential procedure command encounters an empty username.
Note: Patch Management > Patch Alert can alert you—or run an agent procedure—if a machine ID's credential is missing or invalid.
windowsServiceRecoverySettings()
Sets the Service Recovery Settings for any given service in Windows. Specify the name of the service you wish to modify, then set both the first and second restart failure options and any subsequent restart failure options.
Operating systems supported: Windows
writeDirectory()
Writes a selected directory, including subdirectories and files, from Manage Files Stored on Server to the full path directory name specified on the managed machine.
writeFile()
Writes a file selected from Manage Files Stored on Server to the full path filename specified on the managed machine. Enter a new filename if you want the file to be renamed.
Each time a procedure executes the writeFile() command, the agent checks to see if the file is already there or not by hashing the file to verify integrity. If not, the file is written. If the file is already there, the procedure moves to the next step. You can repeatedly run a procedure with writeFile() that sends a large file to a managed machine and know that the VSA only downloads that file once.
Note: Environment variables are acceptable if they are set on a user's machine. For example, using the path %windir%\notepad.exe would be equivalent to C:\windows\notepad.exe.
Note: This command can download files from a LAN file source instead of the VSA using Agent > Configure Agents > LAN Cache. Files have to be larger than 4k bytes.
writeFileFromAgent()
Transfers a file from another agent machine to the agent machine running this step. Transfers a file between agents. Similar to the previous transferFile() step, though in this case you enter the fully qualified machine ID of the source machine that has the file you wish to send to the currently selected agent. First enter the full path and file name of the file you wish to send from the source machine. You then enter the full path and the file name to be created on the target machine.
Operating systems supported: Windows
writeFileInDirectoryPath()
Writes the specified filename to the path returned from a getDirectoryPathFromRegistry() command.
writeProcedureLogEntry()
Writes the supplied string to the Agent Procedure Log for the machine ID executing this agent procedure.
writeTextToFile()
Writes text to a file on the agent machine, either by appending text to an existing file or by creating a new file if none exists. You enter the text to write to the file, then enter the full path and file name on the agent machine the text will be written to. You can optionally overwrite the entire file with the text you have entered if the file already exists.
Operating systems supported: Windows, OS X, Linux
zipDirectory()
Compresses a directory and any subdirectories or files it contains into a zip file on the agent machine. Enter the full path to be compressed, which can contain wildcards. Then enter the full path and file name of the zip file to be created or updated. If the target zip file already exists, optionally check a box to overwrite it.
Operating systems supported: Windows, OS X, Linux
zipFiles()
Compresses a single file or files into a zip file on the agent machine. Enter the full path of the file or files to be compressed. Then enter the full path and filename of the zip file to be created or updated. If the target zip already exists, optionally check a box to overwrite it.
Operating systems supported: Windows, OS X, Linux