Offsite Servers
The Offsite Servers page safely and securely transfers backup images from a LAN to a remote location. Offsite replication transfers all changes to files and sub-directories in the Local Server directory to a specified offsite server directory. File transfers are scheduled using Schedule Transfer. Image Location directories should be defined as subdirectories of a Local Server directory to be included in these transfers.
Offsite Server Configuration
Any machine ID may act as an offsite server. You may also have as many offsite servers as you like. Example Offsite Replication configurations include:
- One global offsite server - A local server at each managed LAN pushes data to the global offsite server.
- Multiple offsite servers - Several local servers are assigned to each offsite server. Multiple offsite servers are used to balance the load.
- Cross offsite servers - Supports offsite replication for companies with multiple locations. For example, two company sites each act as the offsite server location for the other company site.
Offsite Folder Structure
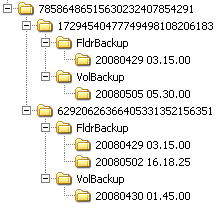
The offsite server stores data received from local servers in the directory specified. The top level GUID folder is the GUID of the local server the data is coming from. Second level GUID folders are the GUIDs of the machine IDs being backed up. The following diagram illustrates a typical offsite server directory structure.
File Transfers
Only file changes are pushed to the offsite server. Broken file transfers are automatically restarted at the point left off. Restarting the file transfer from the beginning is not required. Offsite replication uses the same communications technology used in the agent/server communications. All traffic is 256-bit encrypted.
Using the Same Machine for the Local Server and Offsite Server
You may assign the offsite server to be the same machine as the local server, but note the following:
- You'll need to open a port just to replicate across drives, whereas other replication tools can do so locally.
- The files aren't copied offsite. You'll lose the disaster recovery benefit of an offsite backup.
Setting the Name/IP Address and Port
Select a target machine with an agent that will act as the offsite server. The offsite server is always running and listens for connections from local servers using any TCP port you specify. The port cannot be used by any other application. Try using 5722 as it is similar to the agent checkin port. Offsite server ports are restricted to between 1024 and 49151.
You must specify a DNS name or IP address that can be resolved from the local server. Typically, this is the external name/IP address of the gateway/firewall/router used by the target machine. Configure port range forwarding on your gateway/firewall/router to direct requests for port 5722—or whatever port number you've chosen—to the internal IP address of the machine ID acting as the offsite server.
Note: The offsite server must have a credential set to access the network directory receiving data transfers.
Testing the Offsite Configuration
Once you have configured the offsite server, check pending procedures on the offsite server machine:
- Click the
 or
or  or
or  icon.
icon. - Click the Pending Procedures tab on the Machine Summary page.
- Ensure the
Start Offsite Serverprocedure ran successfully.
Try to connect to the offsite server component using Telnet. In the command below replace the string your.offsiteServer.com with your Name/IP address. Replace 5722 with the port number you are using.
telnet your.offsiteServer.com 5722
If the connection is successful you should see only see a blinking cursor. Once you can verify the offsite server is ready, You can configure the Local Servers.
Synthetic Backups
A synthetic full backup is created by consolidating existing incremental or differential backups with the previous full backup image. This is sometimes called an 'Incremental Forever Backup'. Unlike traditional full backups, synthetic full backups are not transferred from the local server to the offsite server. Instead, after the first full backup is transferred, only the incremental or differential files are transferred to the offsite server. A synthetic backup component on the offsite server recreates the next full synthetic backup in parallel with the local server. This eliminates the need to transfer full backups between the local server and offsite server. With synthetic backups, bandwidth requirements for transferring full backups are eliminated, but the offsite server's access to its own file server may need to be enhanced to handle the processing of its synthetic backups.
Configuring synthetic backups involves the following steps:
Note: The first three steps are required even if synthetic backups are not enabled on the offsite server.
- Install an agent on a local server. Typically the backup image locations of machine IDs being backed up point to the local server.
- Install an agent on the offsite server.
- Define a machine ID as an offsite server using Backup > Offsite Servers.
Note: You do not have to install the backup client to a local server or an offsite server.
- Click the Schedule Install hyperlink on the Backup > Offsite Servers page for the machine ID you want to schedule synthetic support on. A dialog box displays. Schedule the installation of synthetic support components to the offsite server.
- Schedule volume backups for machine IDs, ensure the Synthetic Full checkbox is checked. These are machine IDs that store backups on local servers that transfer backups to the offsite server you defined above.
Create
Click Create to create an offsite server using the options previously selected.
Select Machine ID
Select the machine ID you want to act as the offsite server.
Name/IP
Enter the IP DNS name or IP address of the offsite server.
Port
Enter an unused port number.
Full path to directory (UNC or local) which receives all data transfers
Enter the full path to the directory, either UNC or local, which receives all data transfers. Do not specify an offsite server directory using a mapped drive.
Check-in status
These icons indicate the agent check-in status of each managed machine:
![]() Online but waiting for first audit to complete
Online but waiting for first audit to complete
![]() Agent online
Agent online
![]() Agent online and user currently logged on. Icon displays a tool tip showing the logon name.
Agent online and user currently logged on. Icon displays a tool tip showing the logon name.
![]() Agent online and user currently logged on, but user not active for 10 minutes
Agent online and user currently logged on, but user not active for 10 minutes
![]() Agent is currently offline
Agent is currently offline
![]() Agent has never checked in
Agent has never checked in
![]() Agent is online but remote control has been disabled
Agent is online but remote control has been disabled
![]() The agent has been suspended
The agent has been suspended
Note: Different icon images display when this addon module is installed in a 5.x VSA. The Remote Control > Control Machine page displays a legend of the specific icons your VSA system is using.
Delete Icon
Click the delete icon ![]() to delete an offsite server record.
to delete an offsite server record.
Edit Icon
Click a row's edit icon ![]() to populate header parameters with values from that row. You can edit these values in the header and re-apply them.
to populate header parameters with values from that row. You can edit these values in the header and re-apply them.
Restart Icon
Click the restart icon ![]() to restart a service on a local server or offsite server. You can determine whether this is necessary by displaying the Remote Control > Task Manager process list for a local server or offsite server. You should see
to restart a service on a local server or offsite server. You can determine whether this is necessary by displaying the Remote Control > Task Manager process list for a local server or offsite server. You should see KORepCln.exe running on the local server and KORepSrv.exe running on an offsite server. If not, click the restart icon for the respective local server or offsite server. Other symptoms include:
- One local server is inactive and the others are fine: restart local server.
- All local servers are inactive: restart offsite server.
Machine.Group ID
The list of Machine ID.Group IDs.Organization IDs displayed is based on the Machine ID / Group ID / Organization ID filter and the machine groups the user is authorized to see using System > User Security > Scopes.
Name/IP
The DNS name or IP address used by the offsite server.
Port
The port used by the offsite server.
Directory Path
The directory path used by the offsite server.
Note: Do not specify an offsite server directory using a mapped drive.
Topic 2131: Send Feedback. Download a PDF of this online book from the first topic in the table of contents.