This lab shows how to set up your gateway so it can be accessed by mobile users. You should complete the previous labs to verify the gateway is ready to support the work in this lab.
There are two ways for a client to interact with a gateway:
In all cases, it must be noted that it is possible for a single users BYOD Suite application to access one or more of these two scenarios depending on how a given gateway is defined. So they might access one BYOD gateway using direct, but access another behind the firewall via relay.
Any one gateway might be accessed via direct by employees with VPN solutions, or via relay by devices not allowed on the corporate network.
The bottom line is the mobile clients use the most effective path to reach a gateway, all with tight security.
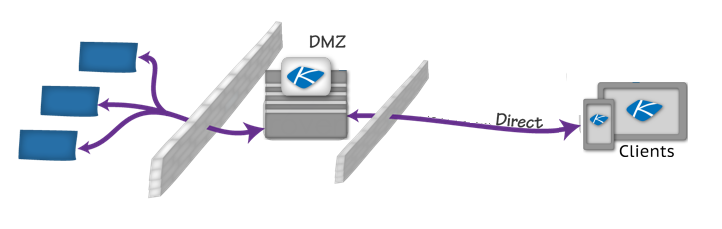
Direct
This option can improve performance for mobiles that are already on the corporate LAN through local WiFi connections or VPN tunnels.
This option also enables corporations to deploy load-balanced clusters of gateways in DMZ’s for high-volume situations, or where a DMZ deployment is preferred.
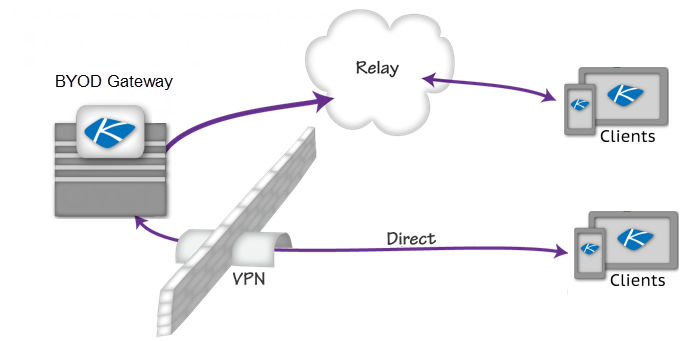
Relay
Relay allows secure exchanges between mobiles and gateways behind a firewall. The mobile devices never become network nodes, increasing security and reducing the need to manage devices. Information is fully encrypted in transit and at rest on the devices for best-in-class protection of your data.
Control Panel Network Configuration
The Control Panel - Network tab is used to configure the BYOD gateway network configuration.
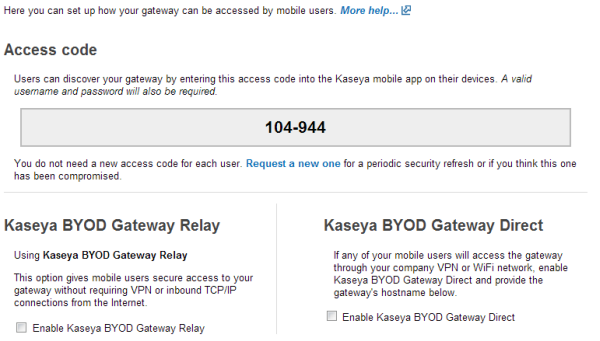
Select the Kaseya BYOD Gateway Relay or Kaseya BYOD Gateway Direct option desired. The Direct option provides a 'test' link to test the connection.
In This Section |